Overview
In the bottom of the foot there is a thick fibrous tissue known as the plantar fascia. The plantar fascia provides stability for the foot and also works as a shock absorber. Injury to the plantar fascia can lead to an aching sensation on the bottom of the foot when walking, especially after long periods of rest. The term plantar fasciitis refers to inflammation on the sole of the foot.
Plantar fascia injuries are most common in individuals who do lots of exercise such as running, jumping and dancing, involving lots of impact on the bottom of the feet. Treatment methods such as massage and rest can help alleviate the painful symptoms. Painful symptoms may ease on their own but if they still remain after 2 weeks, consult a professional.
Anatomy
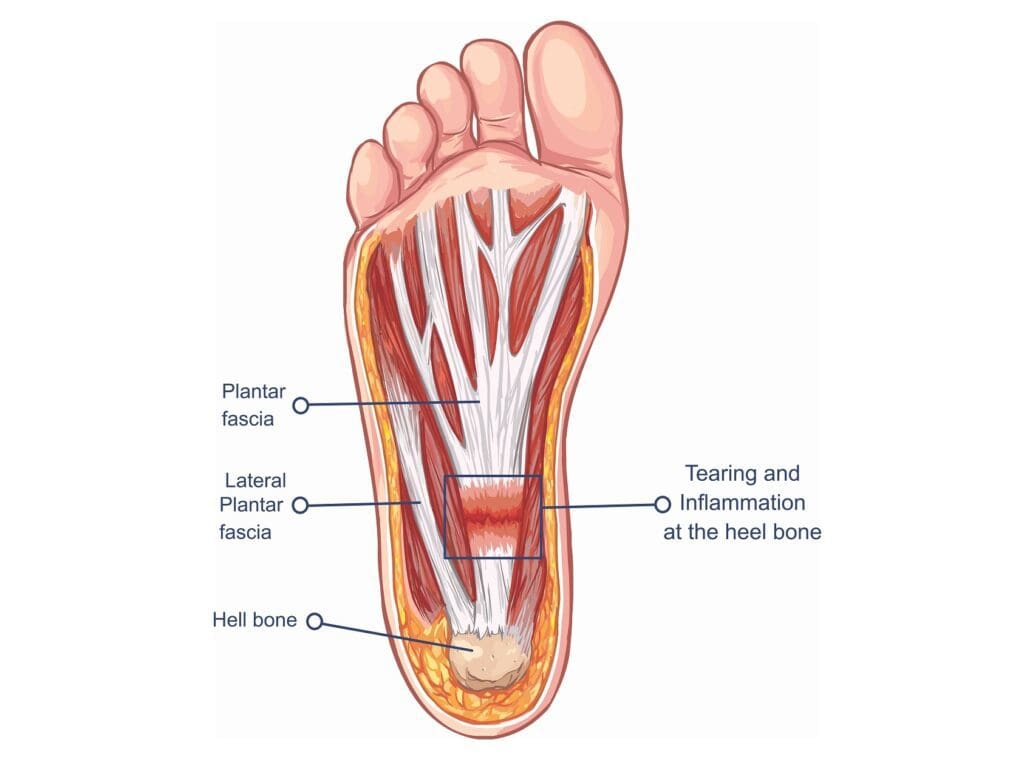
The plantar fascia is a long, thick fibrous tissue connecting to the calcaneus (heel bone of the ankle) it runs along the bottom of the foot and divides into five digital bands, along the heads of the metatarsals (toes). It covers the sole of the foot.
The function of plantar fascia is to provide support to the foot when standing and shock absorption when running.
Inflammation or degeneration of the tendon where the fascia originates can cause heel pain.
Symptoms
The symptoms of plantar fasciitis will be aggravated by continuing activity on the sole of the foot such as walking/running and will get worse over time. Some of the symptoms of plantar fasciitis include:
- Pain on the bottom of the foot, around the heel and the arch (main symptom)
- May be tenderness/pain under sole of foot and under heel when pressing in
- Eases pain when exercising, but painful once rest
- Difficult to raise toes off floor
- Pain occurred gradually
- Pain worse first thing in morning/when walking after long periods of rest
- Pain eases off only to return later
- Pain directly under the heel
- Flat or overpronated feet
- Tight calves
Causes
Plantar fasciitis is directly caused by damage to the plantar fascia running along the sole of the foot.
Some examples of causes/links consist of:
- Overuse
- Recently started exercising on hard surfaces
- Exercising with a tight calf or heel
- Overstretch the sole of your foot during exercise
- Recently started doing a lot more running, walking or standing up
- More common in sports involving running, dancing or jumping
- Foot biomechanics
- Overpronation (foot rolling in/flattening too much when running or walking which stretches plantar fascia more than normal)
- High arch – unable to absorb as much shock so increased strain on plantar fascia
- Footwear – very flat and unsupportive shoes increase likelihood of developing plantar fasciitis
- Bodyweight – overweight individuals or those that do lots of heavy lifting causes increased load on feet increasing chances of developing heel pain
- Flexibility – if have tightness in the calves or plantar fascia this can alter the biomechanics in the foot causing strain on the fascia
Diagnosis
During your visit to your local GP or Sports Therapist / Physiotherapist, they will assess..
- History- how long the pain has been occurring for and when its most painful
- Physical examination- check for tenderness in foot, pain during palpation
- Gait analysis- analysing feet and how they function when walking and running- if overpronate or feet flatten
Treatment
Aims to decrease pain and inflammation, identify and correct possible causes, improve flexibility, gradually increase strength and return to full fitness levels.
- Rest- rest from activities causing the pain reduces initial pain and inflammation
- Massage – can help stretch and relax the plantar fascia. Massage also helps to stimulate blood flow and loosen tight tissues underneath the foot which cause pain
- Stretches – for calf muscles and plantar fascia
- Night splint – compliments plantar fasciitis exercises by preventing the tissues from tightening up overnight. Wearing a night splint is more effective than stretching exercises alone.
- Taping- supports the arch of the foot and reduces strain on the plantar fascia
- Shock Wave Therapy – method of therapeutic treatment for soft tissue injuries- works by passing shock waves into the tissues
- Ultrasound – transmits high frequency sound waves into the tissues- has a micro massage effect and can reduce pain and inflammation
- Footwear – wear comfortable trainers with good cushioning- avoid hard, flat soles
- Cold therapy – ice massage or application of an ice pack for 10 minutes every hour for the first day- reduce to 3-5 times a day as symptoms ease
- Medication – doctor may prescribe NSAID’s (Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) e.g. ibuprofen in the early stages – always check with a doctor before taking any medication
- Orthotics (shoe insoles) – for overpronated feet if feet roll in or overpronate it can cause strain on the foot should be worn at all times, not just when training
- Surgery – rarely needed but is used when all other treatments haven’t helped.
Exercises
The best way to treat plantar fasciitis is firstly to rest. If pain allows, some stretching exercises can help improve symptom’s and alleviate some pain.
- Foot rolling – rolling the foot over a round object such as a ball, weights bar, rolling pin or can of soup can stretch the plantar fascia. Roll the foot repeatedly over the object, applying increasing downward pressure. You can also apply an object that can be cooled in the freezer (bottle or metal can) to apply cold therapy at the same time – 10 minutes per day until walking in the mornings is pain-free.
- Calf stretches
- Soleus stretch
- Stretching on a step – stand with toes on step and heels off the back, lower heels down below the level of the step until a stretch is felt- hold for 15-20 seconds- further stretches calves and Achilles
- Towel Scrunch – While sitting, place a towel on the floor with your foot on top of it. Try scrunching up a towel with your toes like you are trying to pick it up off the floor
No running!
Try to maintain fitness by swimming or cycling & you can begin to start walking again when there has been no pain for at least a week, slowly increase the distance and speed.
Prevention
- Stretching – make sure to keep up the stretching of the lower body to prevent strain on the fascia
- Footwear and Insoles – try to wear shoes that are supportive for the sole of the foot and absorb shock with cushioning
- Ease into more intense exercise gradually – start by walking and gradually increase the amount as time goes on, then eventually ease back into running when pain is eliminated
- Keep a healthy lifestyle and your weight under control as excess weight can increase the amount of stress on the foot



