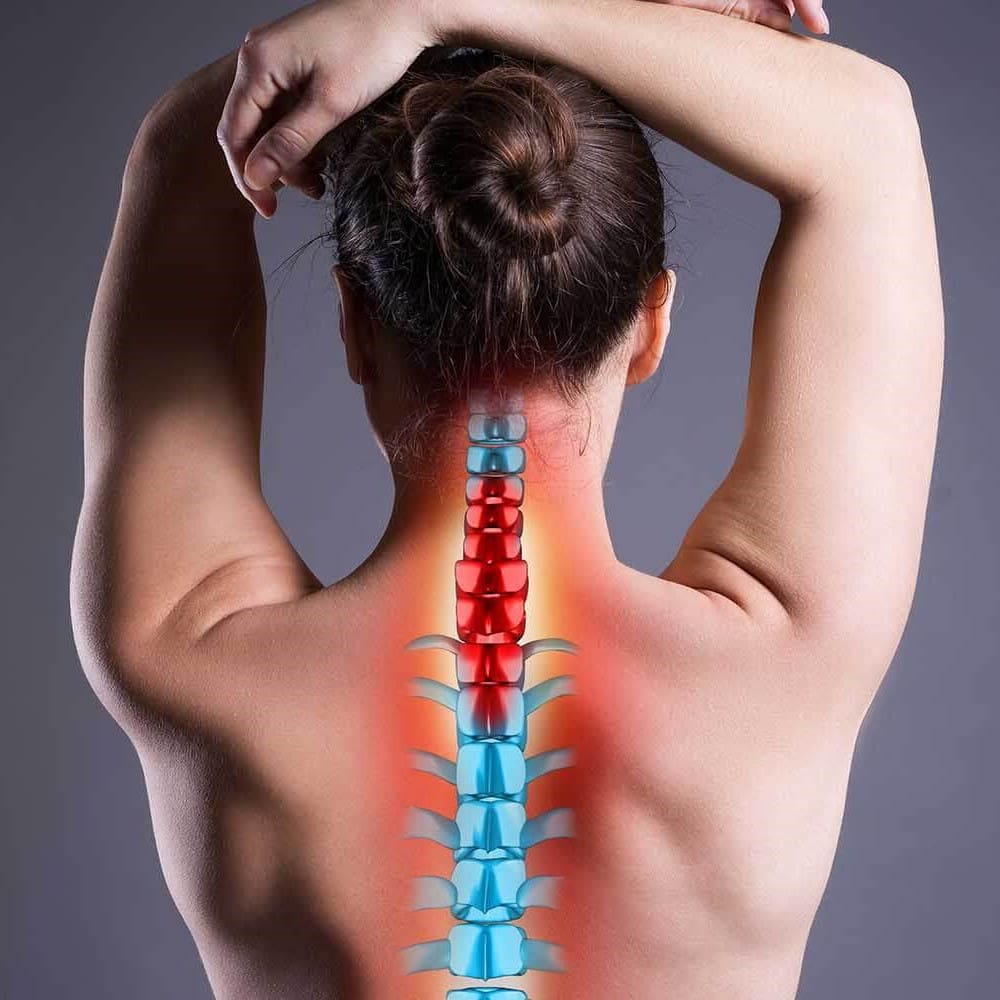
Nerve Impingement
Overview
Nerve impingement, also known as nerve compression or pinched nerve, is a condition in which a nerve is compressed or constricted, leading to pain, weakness, numbness, or tingling sensations in the affected area. This can occur in various parts of the body, including the neck, back, arms, and legs.
The pathology of nerve impingement involves pressure or constriction on the nerve, which can be caused by a variety of factors, such as injury, repetitive motions, poor posture, or degenerative conditions like arthritis. This pressure can lead to irritation and inflammation of the nerve, which can cause pain and other symptoms.
The occurrence of nerve impingement is quite common, especially as people age and degenerative changes occur in the spine. It can also be seen in people who perform repetitive motions or maintain poor posture for extended periods of time. Additionally, nerve impingement can result from injuries, such as whiplash or a herniated disc, or from conditions such as carpal tunnel syndrome or sciatica.
Anatomy
The human nervous system is comprised of a complex network of nerves that run throughout the body, transmitting signals between the brain and various tissues and organs. Nerves are made up of axons, which carry electrical signals, and are surrounded by a layer of protective tissue called myelin. Nerves can be affected by a variety of factors, including compression, entrapment, inflammation, and injury.

Symptoms
The symptoms of nerve impingement can vary depending on the location and severity of the impingement. Common symptoms may include pain, numbness, tingling, burning, or a feeling of pins and needles. In severe cases, nerve impingement can lead to muscle weakness, loss of sensation, and difficulty with movement.
Causes
Nerve impingement can be caused by a variety of factors, including physical trauma, repetitive motions, poor posture, and underlying medical conditions such as arthritis, diabetes, and nerve disorders. Other common causes of nerve impingement include spinal stenosis, herniated discs, and degenerative conditions such as spinal cord injuries.
People who are at a higher risk of developing nerve impingement include:
- Individuals with certain medical conditions such as diabetes, arthritis, or other conditions that can cause nerve damage or inflammation.
- Athletes and physically active individuals who engage in repetitive motions, such as running, cycling, or weightlifting, which can put stress on the nerves.
- People who have a sedentary lifestyle and spend long hours sitting or working in positions that can put pressure on the nerves, such as office workers or truck drivers.
- Individuals with a family history of nerve impingement, as this may suggest a genetic predisposition to the condition.
- People who have suffered a previous injury, such as a fracture or dislocation, that may have damaged the nerves.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of nerve impingement is typically based on a review of medical history, a physical examination, and diagnostic imaging tests such as MRI or CT scans. Nerve conduction studies and electromyography (EMG) tests can also be used to help diagnose nerve impingement and determine the severity of the injury.
It is important to note that while anyone can develop nerve impingement, early detection and proper treatment can greatly reduce the risk of developing long-term complications and help ensure a full recovery.
Treatment
Here are some of the treatment options for nerve impingement:
Rest: Resting the affected area can help reduce inflammation and give the nerve time to heal. You may need to avoid activities that aggravate your symptoms, such as heavy lifting, repetitive motions, or prolonged sitting or standing.
Physical therapy: Physical therapy can help improve your strength, flexibility, and posture, which can relieve pressure on the affected nerve. Your physical therapist may recommend exercises, stretches, or other techniques to help alleviate your symptoms.
Medications: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen or naproxen can help reduce inflammation and relieve pain associated with nerve impingement. In some cases, corticosteroids may be prescribed to reduce inflammation and alleviate symptoms.
Injections: In some cases, injections of corticosteroids or other medications may be given directly into the affected area to reduce inflammation and alleviate symptoms.
Surgery: If conservative treatments are not effective, or if nerve impingement is causing significant weakness or loss of function, surgery may be recommended. The type of surgery will depend on the location and severity of the compression and may involve removing bone or tissue to relieve pressure on the affected nerve.
Lifestyle changes: Making lifestyle changes can help prevent or alleviate nerve impingement. This may include maintaining good posture, staying active, avoiding repetitive motions, and avoiding activities that put excessive strain on your nerves.
Exercises
Exercises to help relieve nerve impingement and prevent further damage may include:
- Stretching: Gentle stretching exercises can help relieve pressure on the nerves and improve flexibility in the affected area.
- Strengthening exercises: Targeting the muscles surrounding the affected nerve can help relieve pressure and prevent further damage.
- Posture correction: Paying attention to posture and correcting any imbalances can help reduce stress on the nerves.
- Aerobic exercises: Engaging in low-impact aerobic activities, such as swimming or walking, can help improve blood flow to the affected area and promote healing.
- Yoga or Pilates: Gentle yoga or Pilates can help improve flexibility and strengthen the muscles surrounding the affected nerve.
It is important to consult with a doctor or physical therapist before beginning any exercise program, as they can help determine which exercises are best for your individual needs and ensure proper form and technique.
Prevention
Maintain Correct Posture:
Be mindful of your posture, especially when sitting or standing for long periods. Maintain a neutral spine position to reduce unnecessary stress on the spine and nerves.
Ergonomics:
Ensure that your workspace, whether at a desk or using electronic devices, is ergonomically designed to support good posture. Use supportive chairs, maintain eye-level screens, and take regular breaks to avoid prolonged periods of the same position.
Regular Exercise:
Engage in regular physical activity to strengthen the muscles that support the spine. Focus on exercises that promote core strength and flexibility, as a strong and flexible spine is less prone to nerve compression.
Correct Lifting Techniques:
When lifting objects, use proper lifting techniques to avoid putting excessive strain on the spine. Bend at the knees, keep the back straight, and lift with the legs rather than the back.
Weight Management:
Maintain a healthy weight to reduce the load on the spine. Excess body weight can contribute to conditions like herniated discs and spinal stenosis, increasing the risk of nerve impingement.
Stay Hydrated:
Hydration is essential for maintaining the elasticity of spinal discs. Dehydration can contribute to disc degeneration, which may increase the risk of nerve compression.
Avoid Repetitive Stress:
Be mindful of repetitive movements or activities that can strain specific nerves. If your work or hobbies involve repetitive motions, take breaks and incorporate stretching exercises to reduce the risk of overuse injuries.
Regular Stretching:
Include regular stretching exercises in your routine to maintain flexibility and prevent muscle imbalances. Focus on stretches that target the muscles around the spine, including the neck, back, and hips.
Quit Smoking:
Smoking has been associated with increased disc degeneration and reduced blood flow to spinal structures. Quitting smoking can contribute to overall spine health.
Proper Nutrition:
Maintain a balanced diet rich in essential nutrients, as proper nutrition supports the health of spinal structures. Calcium and vitamin D are particularly important for bone health.
Regular Check-ups:
Schedule regular check-ups with your healthcare provider to monitor your spine health. Early detection and management of spinal conditions can help prevent the progression to nerve impingement.



